Understanding of Ovarian Cysts After Pregnancy:
Fluid-filled sacs that form on, or inside, the ovaries are called ovarian cysts. These cysts aren’t usually cancerous; however, worrying about having these cysts develop after pregnancy is not uncommon. In this article, I have discussed the symptoms for PCOS, the causes of ovarian cysts, and the available ovarian cyst treatment options to help you to handle this condition with proper care.
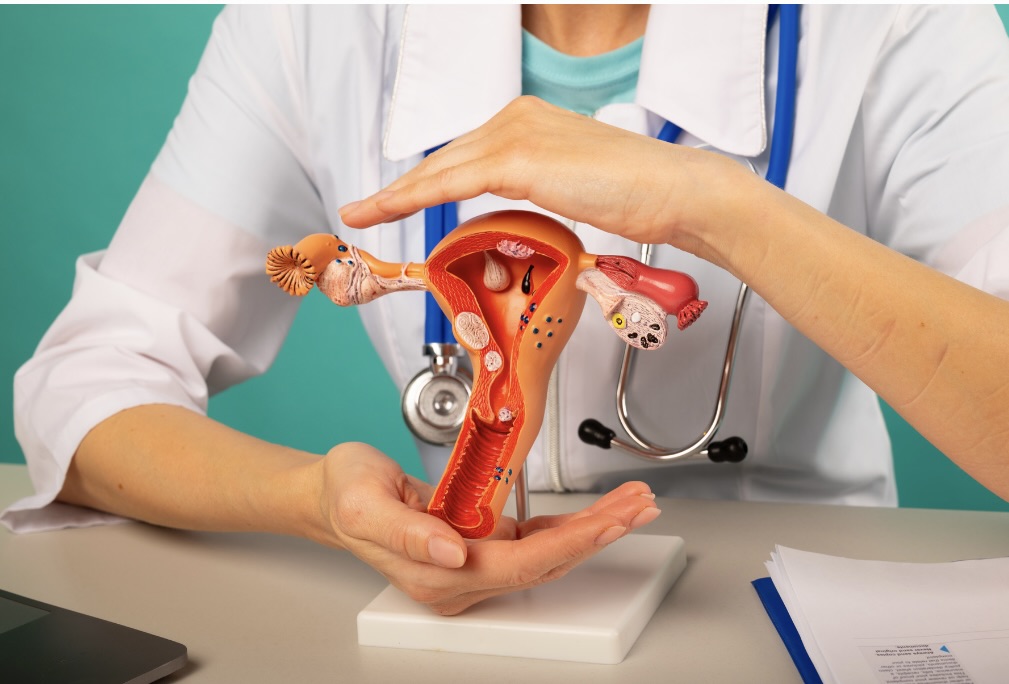
What Are Ovarian Cysts?
Ovarian cyst is a common disease, which may appear during menstruation, or after pregnancy. Often benign (meaning not cancer) and known to resolve themselves, these tumors are not usually cancer. But sometimes, treatment is needed if symptoms for PCOS or cysts persist after you get pregnant. Management of the cyst depends upon knowing what kind of cyst it is and how it develops.
Types of Ovarian Cysts
Several types of ovarian cysts can form, including:
Functional Cysts: These are cysts that happen in the menstrual cycle and usually go away without treatment.
Corpus Luteum Cysts: They form after ovulation when the follicle that releases the egg fills with fluid. These cysts may persist after pregnancy but usually go away on their own.
Dermoid Cysts: Cysts that contain tissue (e.g. hair or skin).
Endometriomas: The cause was cysts formed in the ovaries because of endometriosis, a condition where tissue similar to the inside of the uterus (called uterine lining) grows outside the uterus.
Ovarian Cysts After Pregnancy Causes
Several factors can lead to the formation of ovarian cysts after pregnancy:
Hormonal Changes: Hormonal shifts throughout and post-pregnancy can lead to the formation of ovarian cysts.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Ongoing hormonal imbalances lead to women with PCOS developing ovarian cysts postpartum.
Endometriosis: Ovarian cysts (endometriomas) caused by endometriosis may stay in your body once you've had a baby.
Pelvic Infections: Cysts are a result of infections in the reproductive organs.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts Following Pregnancy
Ovarian cysts are usually asymptomatic, but they can cause pain from larger cysts and ruptured cysts. The symptoms for PCOS or ovarian cysts may include:
Pelvic Pain: It is a common symptom if the cyst is large or ruptured.
Abdominal Bloating: It may also cause a feeling of fullness or pressure in the abdomen.
Pain During Intercourse: Certain women can feel uncomfortable with sexual activity.
Irregular Menstrual Cycles: Ovarian cysts can change your cycle.
Sharp Pain: If the cyst ruptures, it can cause sudden, severe pain and you may need medical treatment.
If you have any of these symptoms for pcos or are worried you may have ovarian cysts, you can visit your local Ovarian Cyst Specialist to check and look after you.
Diagnosing Ovarian Cysts
To diagnose ovarian cysts, your gynecologist may use the following methods:
Pelvic Exam: To find any abnormalities, a physical examination.
Ultrasound: An imaging test that doesn't involve poking or sticking, to find out how big, where, and what kind of cyst you have.
Blood Tests: To see if hormone levels check out or to help rule out other conditions.
CT Scan or MRI: For more complex cases, these imaging techniques are used.
Treatment For Ovarian Cysts After Pregnancy
The vast majority of ovarian cysts don't need to be treated, and particularly functional cysts. However, if the symptoms for pcos causes complications, several treatment options are available:
Watchful Waiting: Many doctors recommend monitoring the cysts with regular ultrasounds to see if the cysts go away by themselves.
Medications: Birth control pills can lengthen the cycle and cause fewer cysts to be created. After breastfeeding, these medications are usually prescribed.
Surgery: A cyst that is large, painful, or suspected of being malignant, may require surgical removal.
Common procedures include:
Laparoscopy: A surgery performed using small incisions to remove the cyst.
Laparotomy: For large or suspicious cysts, a more invasive surgery.
Pain Management: You can take over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen for discomfort.
Treating Underlying Conditions: The good news is that women with PCOS or endometriosis should consider getting treated for these conditions since that may prevent future cysts.
Treatment of Ovarian Cysts After Pregnancy
Severe complications most of the time don't arise from ovarian cysts after pregnancy and often tends to resolve by itself. With regular follow-ups with an ovarian cyst specialist and following medical advice, usual management will be effective. The earlier polycystic ovaries are detected and treated, and the less damage to the normal structures, the fewer complications, and the smoother the recovery will be.
If you’ve developed signs and symptoms of PCOS ovarian cysts and think you may have an ovarian cyst, seek consult with an ovarian cyst specialist for individualized care. But if they do persist in the post-pregnancy period, regular monitoring and prompt treatment will help to manage ovarian cysts and keep reproductive health normal.