Introduction
Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA) is a type of arthritis that affects children under the age of 16. It is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the joints, leading to inflammation, pain, stiffness, and swelling. Unlike in adults, JRA can affect the joints and other organs in the body. The exact cause of JRA is unknown, but genetic and environmental factors may contribute. Symptoms can vary from mild to severe and can affect one or more joints. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to managing symptoms, preventing joint damage, and improving quality of life. Treatment often involves medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes to help children lead active lives. The prognosis can vary depending on the severity and response to treatment.
Cost Comparison
The cost of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis treatment varies widely anywhere in the world, depending on the hospital, the stage of cancer, the type of treatment, the number of therapy sessions required, the patient’s overall health condition, post-operative complications and care, etc. The average cost of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis in India is USD $1800.
But be assured as the cost of Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis in India is just a fraction of developed nations.
- Avg Cost of treatment - $1800
- Maximum cost of treatment - $4300
Factors affecting Cost of treatment
-
Severity and Stage of the Disease: The intensity of the disease (mild, moderate, severe) can affect the type and frequency of treatment required, thus influencing costs. Severe cases may require advanced treatments such as biologics or frequent hospitalizations.
-
Type of Treatment: Treatment options include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologic drugs, and corticosteroids. Biologics tend to be the most expensive option, impacting the overall cost.
-
Duration of Treatment: JRA is a chronic condition that often requires long-term management. The ongoing nature of treatment, including medication and frequent consultations, adds to the cost.
-
Hospital Stay and Follow-Up Visits: Hospital stays (if required) and the frequency of follow-up visits after procedures or treatment will influence the total cost of care. Extended stays or specialized inpatient care can increase expenses.
-
Diagnostic Tests: Blood tests, imaging (X-rays, MRIs), and other diagnostic procedures can incur additional costs, particularly if advanced imaging is needed to monitor the disease progression.
-
Medications: The cost of medications, particularly newer drugs or biologics, can vary. While generic medications may be more affordable, branded and biologic medications used for severe cases are significantly more expensive.
-
Age and Overall Health: The age of the child and their overall health status can affect the treatment approach. Comorbidities or complications may necessitate additional care, leading to higher costs.
-
Healthcare Insurance: The availability of insurance coverage can reduce out-of-pocket expenses. Some families may have insurance that covers a significant portion of the treatment costs, while others may not, which can raise costs significantly.
-
Specialist Consultation: The cost of consulting with pediatric rheumatologists and other specialists may vary depending on their expertise and reputation, further affecting the treatment cost.
Treatment Options
1. Medications
-
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These are often used as a first-line treatment to reduce pain and inflammation. Common NSAIDs include ibuprofen and naproxen.
-
Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): These help slow disease progression and manage inflammation. Methotrexate is commonly used in children with JRA.
-
Biologic Drugs (Biologics): Biologics, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors (e.g., etanercept, adalimumab), interleukin inhibitors (e.g., anakinra, tocilizumab), and other biologics, are often used when other treatments are ineffective, particularly in cases with systemic involvement or severe symptoms.
-
Corticosteroids: Prednisone or methylprednisolone may be prescribed to reduce inflammation during flare-ups or for more severe cases. These may be administered orally, topically, or via injection into affected joints.
2. Physical Therapy
-
Exercise Programs: Specialized physical therapy to maintain or improve joint mobility, strength, and flexibility. Occupational therapy may also be recommended for children to learn ways to manage day-to-day tasks.
-
Stretching: Stretching exercises can help prevent joint stiffness and improve mobility.
3. Joint Injections
-
Corticosteroid Injections: For children with a limited number of affected joints, injections of corticosteroids directly into the joint can provide relief from inflammation and pain.
-
Hyaluronic Acid Injections: In some cases, hyaluronic acid is injected into the joint to improve lubrication and reduce inflammation.
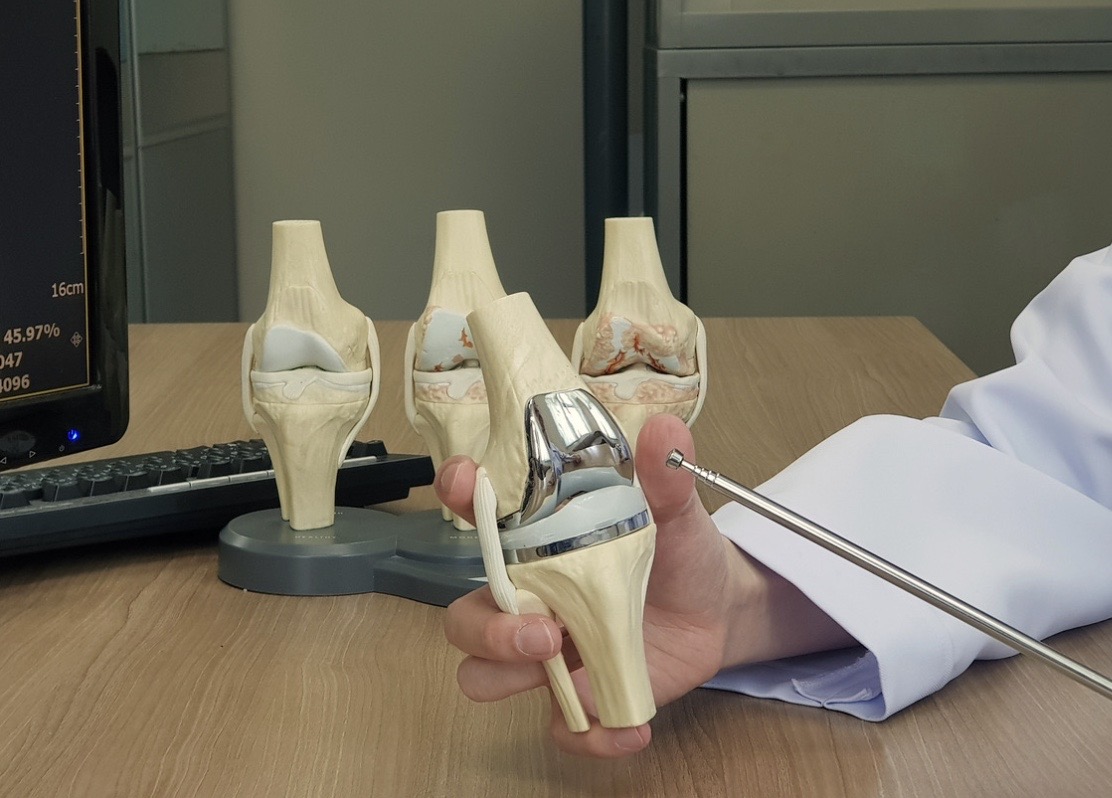
4. Surgical Interventions
-
Arthroscopy: In cases where there is joint damage or severe inflammation, minimally invasive surgery (arthroscopy) may be performed to remove debris from the joint or to clean the joint.
-
Joint Replacement Surgery: In advanced cases where joints are severely damaged and have not responded to other treatments, joint replacement surgery (typically of the hip, knee, or other major joints) may be considered.
5. Dietary and Lifestyle Changes
-
Anti-inflammatory Diet: While no specific diet cures JRA, a balanced diet with anti-inflammatory foods, such as omega-3 fatty acids (from fish), can help reduce inflammation.
-
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the strain on joints, particularly the knees and hips, which are commonly affected by JRA.
6. Alternative and Complementary Therapies
-
Acupuncture: Some children may benefit from acupuncture for pain management, although this should be done under professional supervision.
-
Supplements: Omega-3 fatty acids, calcium, and vitamin D may be recommended to support joint health and bone strength, but should be used under a healthcare provider’s guidance.
7. Regular Monitoring and Follow-up Care
-
Routine check-ups with pediatric rheumatologists and regular blood tests are essential to monitor disease activity and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
-
The treatment plan is often personalized to address the child’s specific needs and the severity of their JRA.
8. Psychological Support
-
Children with chronic illnesses such as JRA may benefit from psychological support to help them cope with the emotional and mental health aspects of living with a chronic condition. Counseling or support groups can provide help to both the child and their family.
How Medotil Global Assists International Patients
Medical Visa Assistance
- Guides patients through the process of obtaining a medical visa for India.
- Provides necessary documentation support, such as invitation letters from hospitals.
Accommodation Arrangements
- Helps secure comfortable and affordable lodging near treatment centers.
- Offers a range of options, including guest houses, hotels, or serviced apartments.
Food Services
- Assists in arranging dietary preferences, including international cuisines and special diets for medical needs.
Transportation Support
- Provides airport pickup and drop-off services.
- Offers reliable transportation for hospital visits and local travel.
Hospital and Doctor Selection
- Recommends top hospitals and connects patients with experienced specialists in their specific condition.
- Ensures access to advanced medical treatments and technology.
Tourism Services
- Organizes visits to famous tourist attractions like the Taj Mahal, Jaipur, Kerala, and other cultural landmarks.
- Tailors travel plans based on patient preferences and recovery needs.
24/7 Support
- Provides round-the-clock assistance for any queries or emergencies during the stay in India.